Software Patterns
The following are my notes are from Design Patterns.
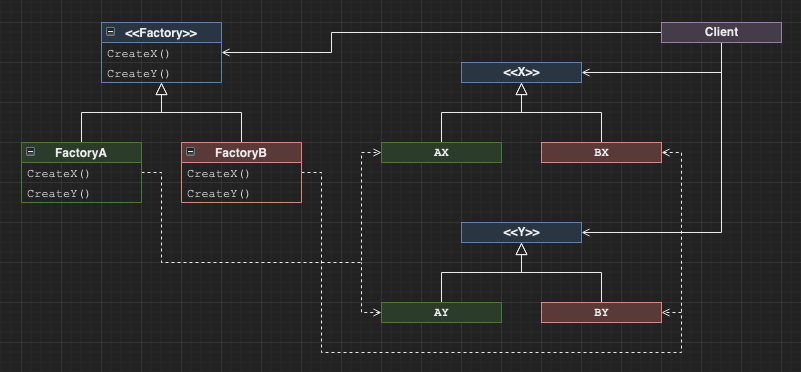
Abstract Factory
Allows a client to produce objects with a common interface without knowing any details about the produced objects except for thier interface.
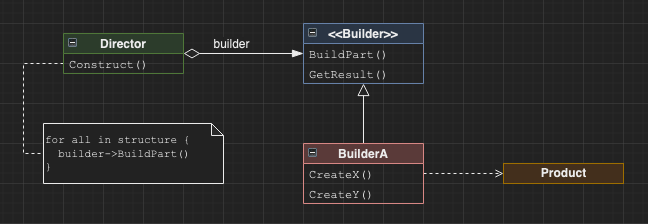
Builder
Allows a class to construct an object in steps using a common interface.
Use cases I’ve used builder for:
- configurable/flexable systems
- e.g. the construction of a simulated robot with varying number of sensors/actuators
- integration test harness configuration
- e.g. instantiate a test including users Bob with $100 and Charlie with $200
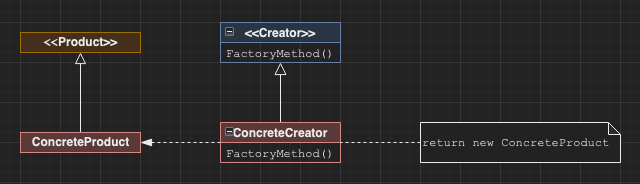
Factory Method
Specifies a factory method interface which concrete factories inherit from. Decouples the user of the factory from the specifics of what it produces.
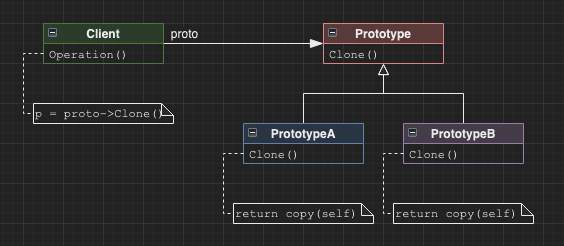
Prototype
Allows the production of objects through prototypes without knowing the exact concrete class.
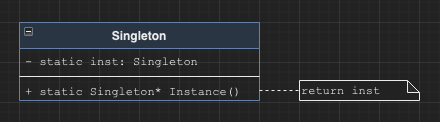
Singleton
Use static class tricks to ensure only one instance of a class exists. Can be useful for doing things like ensuring there is only one source of truth for time. Singletons often have the same disadvantages as global state - can be especially annoying in testing.
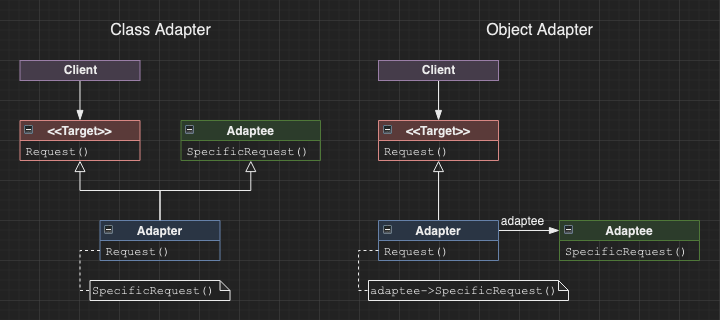
Adaptor
Also known as wrapper. A class which adapts the functionality of another class to a desired interface.
This is achieved in two ways:
- Class adaptor
- Inherit from both the desired interface and the adaptee class. Provide the desired interface through calls to the adaptee parent class.
- May simplify the adaption through access to protected members and allowing overriding where necessary.
- Object adaptor
- Inherit from the desired interface only. Use object composition to access the adaptee interface.
- Allows situations where the desired interface is better acheived through a combination of classes.
- Preferred choice when we want to adapt a class and all of its subclasses.
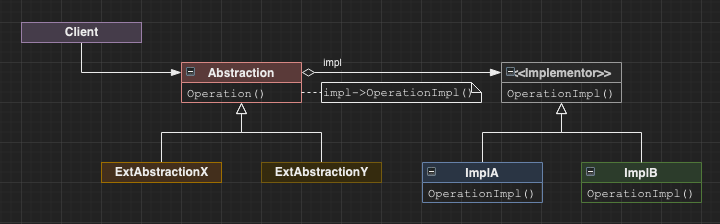
Bridge
Decouples a public interface from implementation. This is useful for unstable interfaces, or interfaces which need to be extended without necessarily changing the underlying implementation.
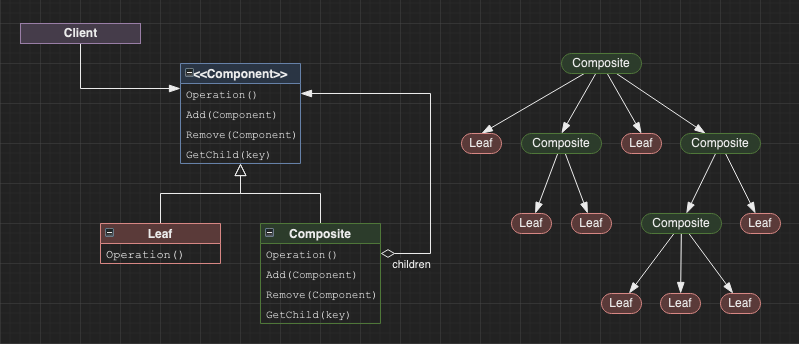
Composite
Specifies a common interface for both primitive objects and compositions of objects so that the objects can be represented in part-whole tree structure heirachies.
Generally useful for grouping objects into a heirachical model.
A potential use case is running a multi-model simulation where the simulation state is propagated between compositions and primitive models.
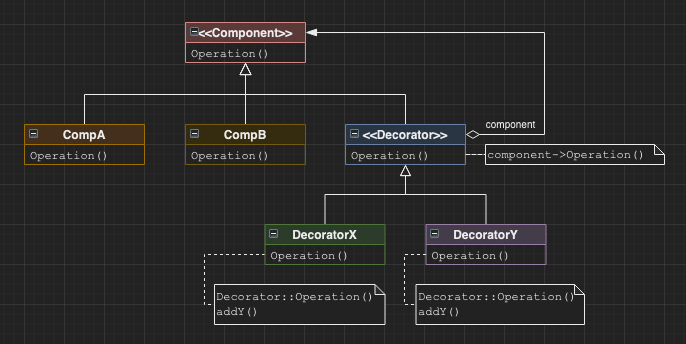
Decorator
Allows dynamic allocation of responsibility to objects (not classes) through decorator objects.
A decorator shares the interface of a target object, and then uses the target object as a delegate with the option of extending behaviour where necessary to acheive the decorator’s reponsibility.
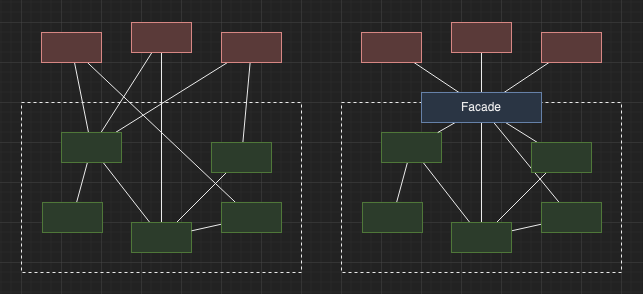
Facade
Provides a high-level interface to a subsystem.
- Simplifies interactions between sub-systems
- Allows sub-systems to be interchanged through a common interface
- Can be used with abstract factory when subsystems are to be used interchangably
- e.g. logging protocol, ODE solver, communication framework etc.
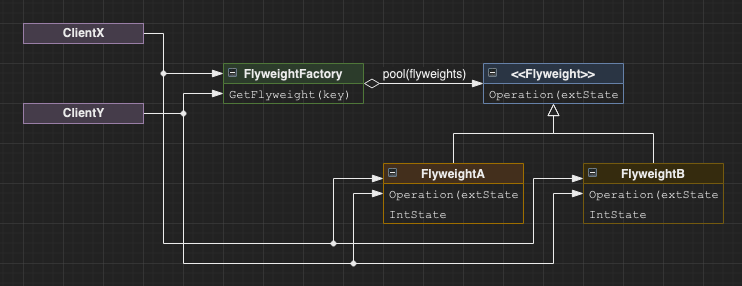
Flyweight
An optimization used to reduce storage cost of potentially prolific but identical objects.
Use a pool of shared objects which are commonly used throughout an application.
The objects generally hold some intrinsic state that is useful across all clients and are handed temporary extrinsic state in which to operate on when used by a client.
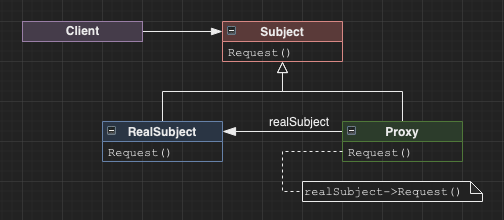
Proxy
A class which takes requests on behalf of a subject to control access to that subject. Applications are:
- remote proxy - hide the fact that the Subject is on a different address space to the rest of the application
- virtual proxy - lazily instantiate objects only when necessary, often as a memory/cpu optimization
- protection/smart reference proxy - apply additional controls, operations, or filtering to requests.
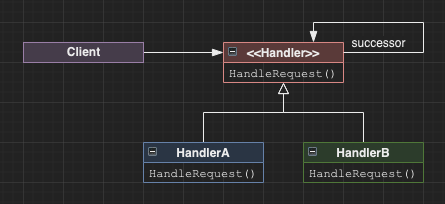
Chain of responsibility
The chain of responsibility allows an event to be handled across a context-sensitive chain of instances. The request is terminated at the first handling of that event. The sender is decoupled from the implicit receiver of the event.
Commonly used with composite where unhandled requests propagate towards the root of the tree.
For example, the action key in a video game may trigger a selection in a menu, open a chest, or cause a player to attack - all of which may be valid actions in a given context; however with a menu open, we probably don’t want to open the chest or initiate an attack.
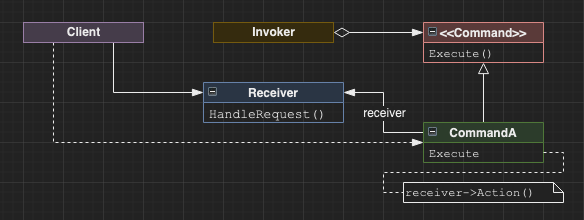
Command
Decouples the invoker of a request from the request itself and the receiver of the request. Allows arbitrary numbers of requests to be added to an invoker and dynamic adding/removing of requests.
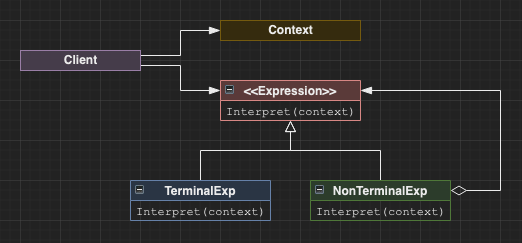
Interpreter
Uses an abstract syntax tree to traverse and interpret a language (usually a dsl).
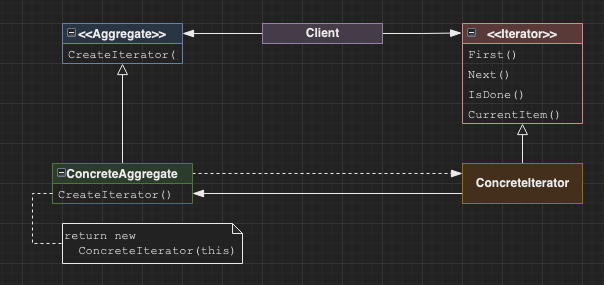
Iterator
Separate the traversal of an aggregate (list, map, set, etc) from the storage of the aggregate. Allows some abstraction so that iterators of different aggregates may share an interface. Also allows various iteratation algorithms.
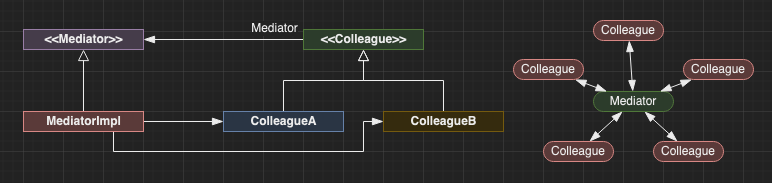
Mediator
Decouples a group of objects from thier interactions with eachother. Allows complex interactions to be handled as the responsibility of the mediator, rather than distributed thoughout many colleague objects.
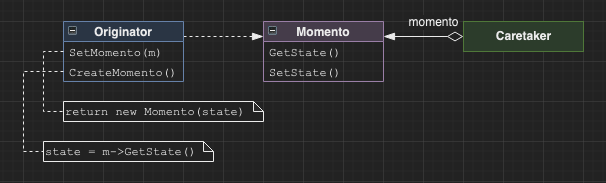
Memento
Opaquely capture the relevant state of an object so that object can be restored to that state if necessary.
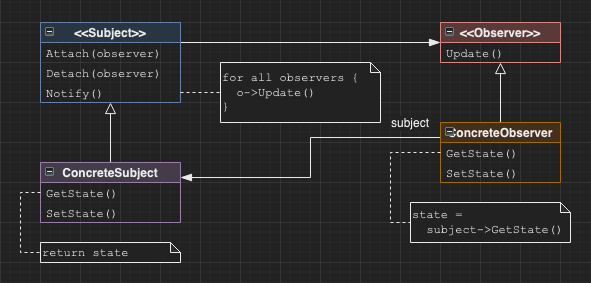
Observer
Involves a single subject and one or more observers which are notified when the state of the subject changes. Allows an arbitrary and dynmaic number of observers. Very similar to publish-subscribe.
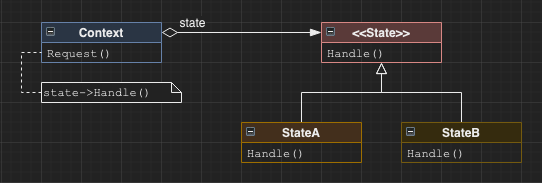
State
Have an object delegate some of its behaviour to state objects. When state changes, the state delegate is changed accordingly. Allows an object to have arbitrarily extendable state.
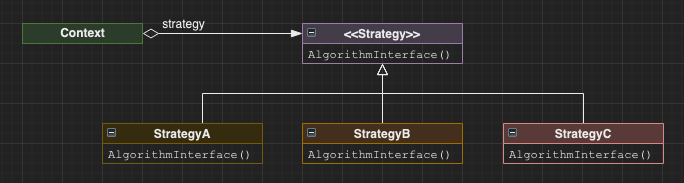
Strategy
Provide a common algorithm interface so that the underlying algorithm used can be exchanged depending on the context of what needs to be achieved. This might be useful for example when computing mortgage rates depending on various vendors.
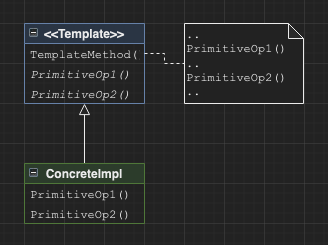
Template method
Implements the invariant parts of an algorithm in an abstract parent class, and lets subclasses fill in the variant functionality.
A potential usecase is handling message payloads, where subclasses effectively handle the encoding strategy (JSON, YAML, etc), while the parent class handles general message logic.
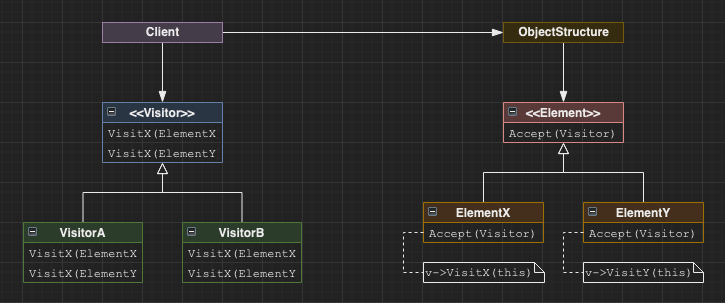
Visitor
Allows us to perform operations on objects in an object structure. Visitor supports objects of multiple classes, but will need to know about each class.
Useful when we want to separate the responsibility of the operations performed on an object structure from the objects in the strucure itself. Instead the objects in the structure are just responsible for accepting visitors.